To Buy Bimatoprost Online Visit Our Pharmacy ↓

Bimatoprost was first approved by the FDA in 2001 under the trade name Lumigan, developed by Allergan Inc., initially intended to treat high intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Its discovery was part of a broader quest to develop more effective and safer treatments for these conditions, marking a significant advance in ophthalmic medication. Bimatoprost belongs to a class of medications known as prostaglandin analogs, substances that mimic the action of prostaglandins, which are naturally occurring fatty acids involved in several physiological functions, including the regulation of intraocular pressure.
The development of bimatoprost was groundbreaking, as it offered a novel mechanism of action compared to traditional glaucoma therapies. By increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways, bimatoprost effectively reduces intraocular pressure, a critical factor in the management of glaucoma. Its origins are rooted in extensive pharmacological research aimed at understanding and manipulating the pathways involved in eye pressure regulation. This focus on innovative approaches to therapy paved the way for bimatoprost to become a cornerstone in glaucoma management, highlighting its importance in the therapeutic landscape.
The Mechanism Behind Bimatoprost: How It Works
Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostaglandin analog that mimics the effects of naturally occurring prostamides. Its primary mechanism of action for treating glaucoma involves increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways, effectively reducing intraocular pressure (IOP). By targeting these specific outflow pathways, bimatoprost helps to alleviate the pressure buildup that can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss in glaucoma patients. Its targeted approach distinguishes it from other IOP-lowering medications that may decrease aqueous humor production or have less specificity in increasing outflow.
Despite its potent IOP-lowering effects, the precise underlying mechanisms of bimatoprost at the molecular level are not fully understood, suggesting areas for further research. What is known, however, is that its ability to bind to prostaglandin receptors in the eye promotes increased drainage of the aqueous humor, thereby achieving its therapeutic effect. This action is critical for patients with glaucoma, where effectively reducing eye pressure can slow the progression of the disease and help preserve eyesight. The specificity and efficacy of bimatoprost in enhancing aqueous humor outflow make it a valuable component of glaucoma management strategies.
Bimatoprost Vs. Traditional Therapies: a Comparative Analysis
Bimatoprost represents a significant advancement in glaucoma therapy, offering an effective alternative to traditional treatments. Where traditional medications primarily aim to decrease intraocular pressure by either reducing the production of aqueous humor or by improving its outflow, bimatoprost, a prostaglandin analog, specifically targets the outflow pathway, enhancing uveoscleral outflow. This mechanism significantly differs from beta-blockers or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, making bimatoprost a preferred option for patients not responding well to other therapies. Its efficacy in lowering intraocular pressure more consistently across diverse patient populations marks a notable improvement over traditional options.
However, the comparison extends beyond efficacy. The adoption of bimatoprost over traditional therapies is also influenced by its user-friendly once-daily dosing schedule, which contrasts with the more frequent dosing requirements of some traditional therapies, potentially improving compliance. Nevertheless, it's crucial to consider the economic aspect, as the cost of bimatoprost may be higher, posing a challenge for some patients. Despite this, its significant benefits, including a potentially lower risk of systemic side effects compared to beta-blockers, position bimatoprost as a critically important option in the management of glaucoma.
The Lifesaving Impact: Bimatoprost on Glaucoma Patients
Bimatoprost has significantly altered the landscape of glaucoma management, offering new hope to those affected by this potentially blinding condition. By enhancing aqueous humor outflow through both the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways, bimatoprost lowers intraocular pressure (IOP), a critical factor in glaucoma treatment. Its efficacy in reducing IOP where other medications have failed has made it a cornerstone in the therapy of various forms of glaucoma, effectively slowing the progression of the disease and preserving the vision of countless patients. Its role in patient care has been transformative, bridging the gap where traditional therapies have not sufficed and providing a lifeline for those at risk of losing their sight.
However, the true impact of Bimatoprost extends beyond its pharmacological benefits. The psychological and quality-of-life improvements for patients cannot be overstated. With the threat of vision loss significantly reduced, individuals are able to lead fuller, less restricted lives. Additionally, the ease of use, involving just once-daily topical application, enhances compliance among patients, a crucial aspect of long-term management of glaucoma. Despite potential side effects, the positive outcomes associated with its use underscore a major advancement in ophthalmic care. As such, Bimatoprost represents a pivotal development in the ongoing fight against glaucoma, offering a blend of efficacy and hope that was previously unattainable with older treatment modalities.
Addressing Side Effects: the Other Side of Bimatoprost
While bimatoprost presents a significant advancement in glaucoma treatment, it is not without its drawbacks, primarily in the form of side effects. Commonly reported adverse effects include conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, and eyelash growth, with less frequent issues such as skin darkening around the eyes, dry eyes, and ocular irritation. These side effects, though often not severe, can impact patient compliance and quality of life. It is crucial for healthcare providers to discuss these potential side effects with patients, offering a complete picture of what treatment may entail.
In addressing the side effects of bimatoprost, research and patient feedback have guided the development of management strategies and formulations aimed at reducing discomfort and increasing tolerance. For instance, lower concentration formulations and the careful application of the medication can minimize exposure and reduce the risk of adverse effects. Moreover, ongoing research into the delivery methodologies and alternative medications continues to prioritize efficacy while aiming to mitigate side effects, ensuring that patient care and comfort remain at the forefront of glaucoma treatment strategies.
The Future of Glaucoma Treatment: Beyond Bimatoprost
As the medical community continues exploring innovative glaucoma treatments, emerging therapies and technologies promise to revolutionize patient care. Research is underway on novel drug formulations and delivery systems, such as sustained-release implants, which could offer more convenience and efficiency than daily eye drops, thereby improving patient compliance and treatment outcomes. Additionally, gene therapy presents a futuristic avenue, targeting the fundamental genetic causes of glaucoma to prevent or significantly decelerate disease progression. These advancements signify a move towards personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patients’ genetic profiles and disease mechanisms, potentially offering more targeted and effective care.
On the technological frontier, advancements in bioengineering and nanotechnology are paving the way for cutting-edge devices and materials that could be used in glaucoma management. Micro-scale devices, capable of monitoring intraocular pressure in real-time and delivering drugs on-demand, are in development. This could lead to a paradigm shift in how glaucoma is monitored and treated, making disease management more proactive rather than reactive. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being harnessed to improve diagnostic precision and predict disease progression, facilitating earlier intervention and better management of glaucoma. Collectively, these innovations herald a future where glaucoma treatment is more effective, less invasive, and highly personalized.
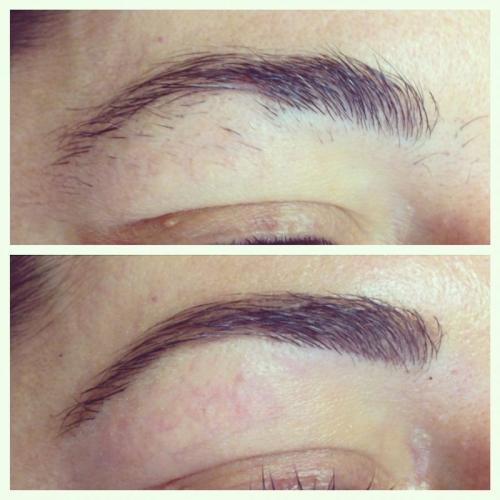
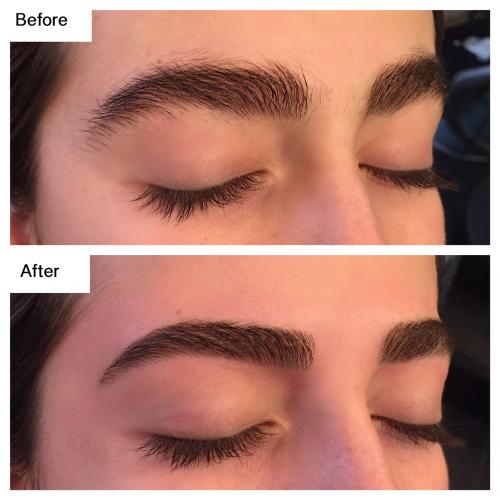
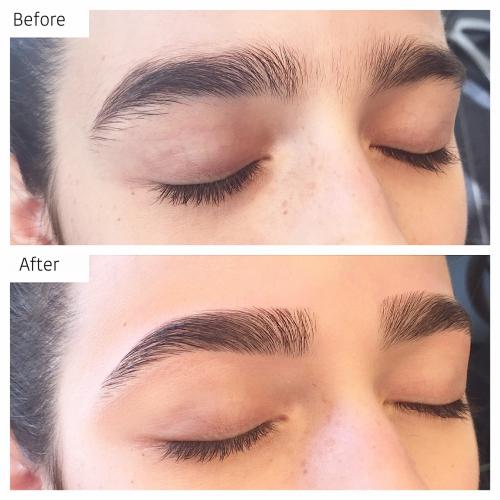
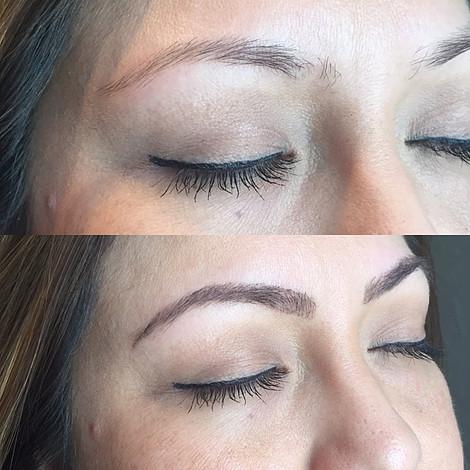
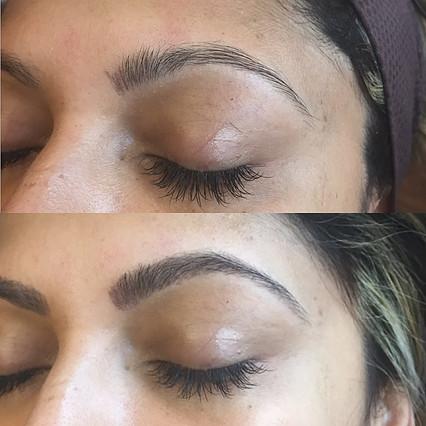
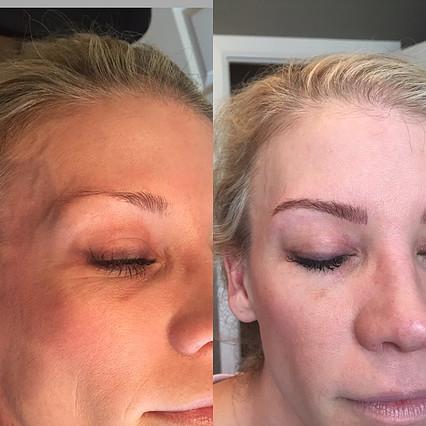
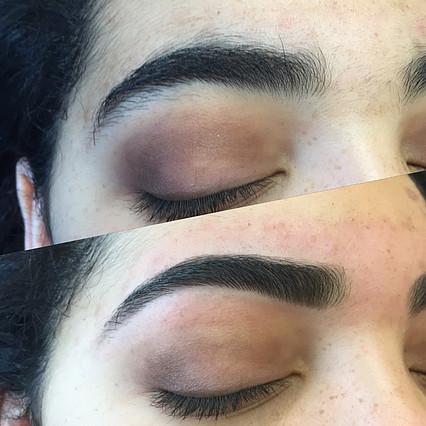
Before & After
Testimonials
Read out what our customers say about our services.
Read Testimonials
Join Our VIP List
Great News!
Comming soon our new location in Fort Worth (Alliance area)
3529 Heritage Trace Parkway, Suite 163
Fort Worth, TX 76244
Sign up now to join our VIP list and receive coupons